A credit card payment is normally granted by a credit card within several seconds. Your company may receive numerous credit cards monthly from clients. In fact, there is a lot of interaction between various parties at play. After learning the roles of each player, you can begin finding new ways to improve your payment system.
What is a payment processor?
Payment processing is essential in online or in-person retail sales. The processor transfers data to you and the merchant acquirer to the issuing bank for payment throughout the transaction. Brick-and-mortar business processes payments using the point-of-sale terminal that reads EMV cards. When customers use their cards personally, their cards are validated, and information is sent through the POS to the issuing bank, which accepts the transaction as an authorized. Once the payment process is finished, the terminal is given the status of payment.
What is a credit card processing company?
I want to explain the different terms processors are used to describe banks. Credit card processors, or simply processors for short, act as intermediaries for merchant accounts and other financial institutions. These third parties could be direct processors (i.e. independent sales organisations). Occasionally a processor will provide a merchant with equipment needed for transaction facilitation. It is possible also to support data security solutions and PCI compliance services.
What are Acquiring Banks?
A Merchant Acquirer Bank is a Merchant Bank. It is a financial institution that provides credit card transactions for merchants that require credit cards. Acquired banking systems settle merchant transactions on their own bank accounts. In certain situations, credit card processing and bank accounts are similar. However, this can sometimes be wrong. This includes managing all aspects of merchant services. They accept cards, debit cards, or credit cards.
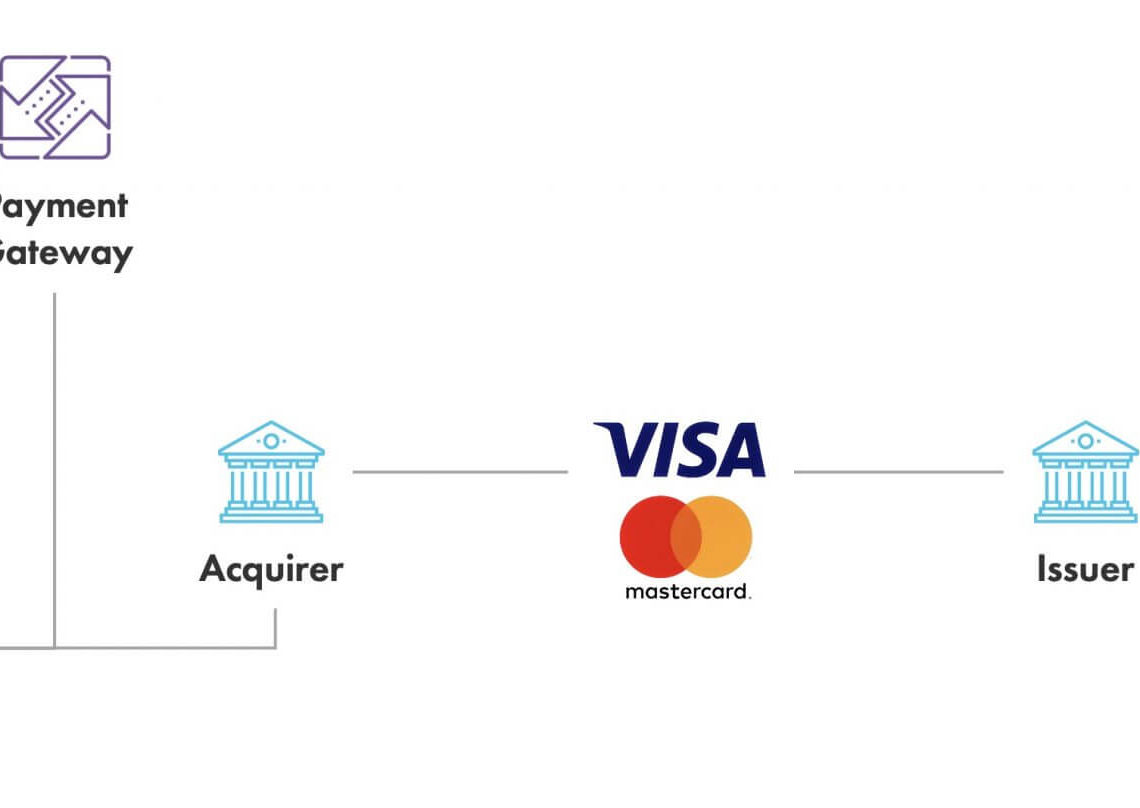
Understanding the differences between acquirers, issuers and payment processors
It is required that you use a payment processor for accepting digital payment transactions. However, some of the terms mentioned in this text are incorrectly employed. This paper examines how credit card transactions are managed throughout the credit card lifecycle to eliminate misunderstandings.
Acquirer vs. issuer
Confusion has erupted concerning the difference between the acquirer and the issuer. The issuer or distributing bank are the banks of the cardholders. It is responsible for paying a credit card approval fee to the merchant acquirer if the card was issued or collected from the card. Also, the issuing bank was the bank to which cardholders were connected. The acquisition bank is the bank with which the merchant is affiliated. The issuing bank takes cardholders’ responsibility. A payment gateway or payment facilitator is a term that is sometimes mistakenly confused with the payment processor.
Acquirer vs. payment processor
Acquisition processors and payment processors often have interchangeable terms. Payment processing providers work in conjunction with merchants, bank accounts, or card networks. These are logged and transmitted by card networks or banks as payment data. In some instances, the processing company will also offer payment terminals used by merchants to make payments. Most advanced payment services integrate with your ERP systems. You could also record payments from any channel and store the data together.
Tell me the difference between acquiring a credit card and acquiring a bank.
One financial institution may act as a processor or acquirer in some circumstances. In these conditions, they are not different. The processing company also assumes that the acquiree is a completely separate company. I’m going to explain how credit card roles are different.
Card networks and issuer banks
The acquiring bank is an intermediary between merchants on card networks and issued banks. The issuing bank is the bank of cardholders. Card networks offer real cards and services to cardholders. The issuing banks are responsible for paying acquiring companies. Technically speaking, the cardholder doesn’t pay the store directly — even when dipping or swiping the cards at the cashier’s terminal. Behind the scenes, the issuing bank pays its acquirer bank, resulting in the business gaining cash into the merchant’s bank account. Transactions are handled, however by a processor.
Security
Data security on cards is dominated by processors or a merchant of record. As processors are responsible for providing hardware for retailers, the processors are also responsible for ensuring that the product’s security continues. Despite this, banks will still be required by security standards to operate. They also collect sensitive card information. Nevertheless, all security to acquire banks is distinct from the merchants. Acquiring bank security is managed by the company and provides no guarantee to retailers. In general, every merchant will have to ensure that security is in place.
Relationship with merchants
Payment services providers, merchant acquirers and payment facilitators have a special relationship with merchants. The processor of the credit card usually has more direct involvement with the merchants. This makes these accounts also called merchants. They call you every time you switch accounts. When you first start using credit cards you may need a credit processing service. It’s impossible to get in touch with a acquiring institution. Possibly there is no specific contact at the institution.
Software and hardware
Most often, all necessary software is supplied by a card processor. They offer everything from terminal cards to terminals, e-commerce gateway systems, and virtual terminals. Payment facilitators and processors will also connect your account to the payment processing platform required to authorize the transaction. Ensure your payment provider accepts online payments from merchant accounts.